https://linuxize.com/post/how-to-install-flask-on-ubuntu-20-04/
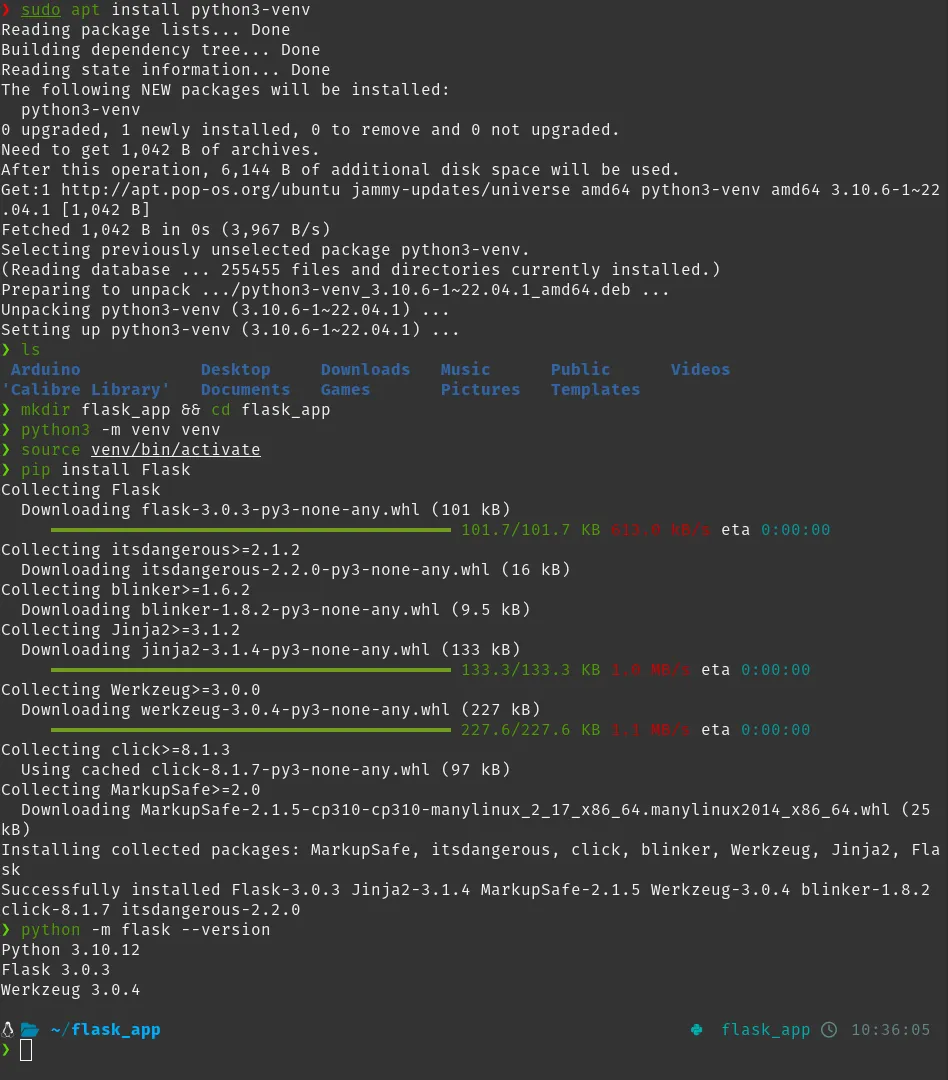
sudo apt install python3-venv
Navigate to the directory where you want to store the Python 3 virtual environments. It can be your home directory or any other directory where your user has read and write permissions.
Create a new directory for the Flask application and switch into it:
mkdir flask_app && cd flask_app
Run the following command inside the directory to create the virtual environment:
python3 -m venv venv
The command will create a directory called venv, which contains a copy of the Python binary, the Pip package manager , the standard Python library, and other supporting files. You can use any name you want for the virtual environment.
To start using the virtual environment, you need to activate it with the activate script:
source venv/bin/activate
Once activated, the virtual environment’s bin directory will be added at the beginning of the $PATH variable. Your shell’s prompt will also change and show the name of the virtual environment you’re currently using. In this example that is venv.
Now that the virtual environment is activated, use the Python package manager pip to install Flask:
pip install Flask
Within the virtual environment, you can use the command pip instead of pip3 and python instead of python3.
To verify the installation, run the following command, which prints the Flask version:
python -m flask --version
At the time of writing this article, the latest official Flask version is 1.1.2
Python 3.8.5
Flask 1.1.2
Werkzeug 1.0.1Your Flask version may differ from the version shown in this example.
Install Django
In a new terminal (if you want) Do that
source my_env/bin/activate
source venv/bin/activate

Then do
pip install django
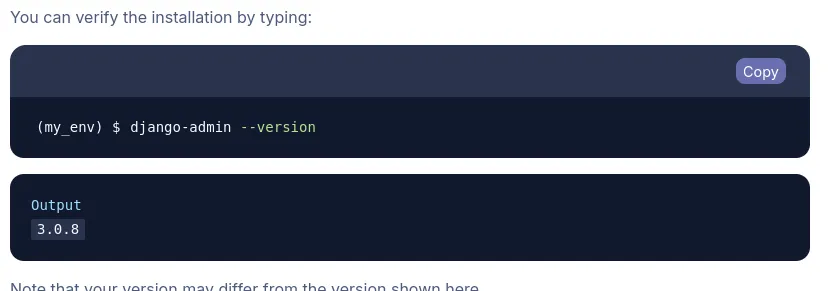
To verify
django-admin --version
Leave virtual environnement
deactivate
Test the Flask
https://linuxize.com/post/how-to-install-flask-on-ubuntu-20-04/ ~/flask_app/hello.py
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello_world():
return 'Hello World!'
Run it
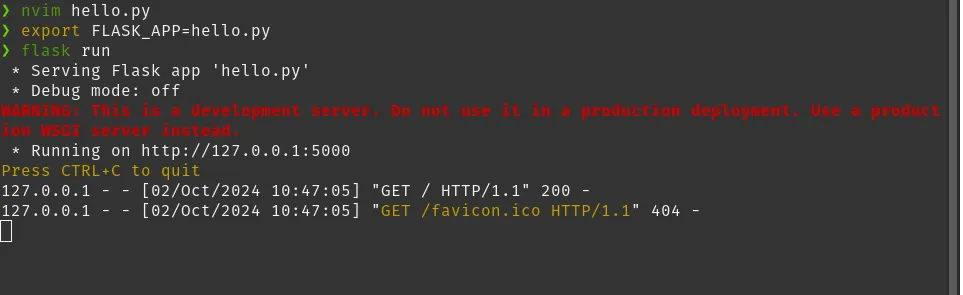
export FLASK_APP=hello.py
flask run
Create a Django project
- Create a Django Project: First, create a new Django project using the following command in your terminal:
django-admin startproject myproject
This will create a directory structure for your Django project.
- Create a Django App: Inside the project directory, create a new app:
python manage.py startapp myapp
This app will contain the views and routes.